Appearance
函数也是对象,因此函数也是存储在堆内存,声明函数除了基础篇章说的函数表达式,和函数声明两种方式外,也可以 'new'出来,但这种方式不推荐
js
var sum = new Function('num1','return num1')
console.log(sum(10)) // 10
var foo = function() {} // 堆内存
function bar() {} // 堆内存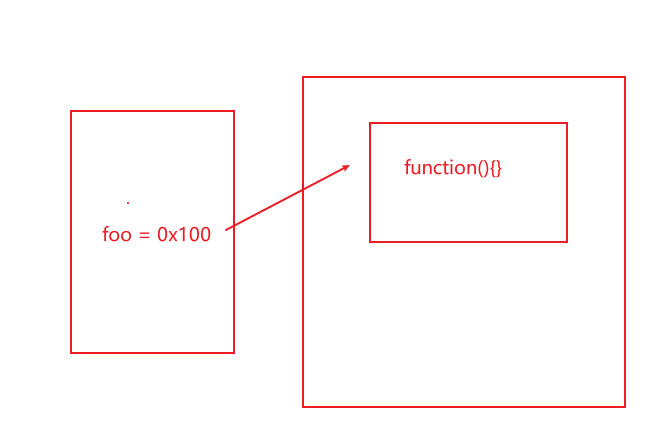
length 属性
函数作为对象因此也是具备对象可以调用属性的使用形式 其中 以length 为例 MDN
- MDN 里面解释:length 属性指明函数的形参个数。
- 'arguments.length' 是函数被调用时实际传参的个数,'Function.length'指该函数有多少个必须要传入的参数,即形参的个数
MDN 上的案例
js
console.log(Function.length); // 1
console.log((function() {}).length); // 0
console.log((function(a) {}).length); // 1
console.log((function(a, b) {}).length); // 2
// 0,不计算不定参数
console.log((function(...args) {}).length);
// 1,只有在第一个参数之前
// a 形参计算默认值,只能算出a的参数
console.log((function(a, b = 1, c) {}).length); // 1Function -- arguments
- arguments 是一个 对应于 传递给函数的参数 的 类数组 array-like对象
- arguments 只是像数组结构一种对象,因此他不具备数组的方法,如filter、map,但其自身是有length,且也是可迭代对象,因此可以使用index 依次获取或者 of循环可迭代对象
- arguments 获取是是实际传入参数个数
js
function a(p1, p2, p3, p4 = 4, ...args) {
console.log(arguments)
console.log(arguments.length)
}
a() // [Arguments] {} 0
a(1, 2) // [Arguments] { '0': 1, '1': 2 } 2
a(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7) // [Arguments] { '0': 1, '1': 2, '2': 3, '3': 4, '4': 5, '5': 6, '6': 7 } 7arguments转Array
- 遍历arguments,添加到一个新数组中
- 调用数组slice函数的call方法
- ES6 Array.from 和 解构赋值
js
function a(p1, p2, p3, p4 = 4, ...args) {
const newLs1 = []
for (let item of arguments) {
newLs1.push(item)
}
// es6
const newLs2 = Array.from(arguments)
const newLs3 = [...arguments]
// 改变this 指向 等同 [].slice.call(arguments) 等同 arguments.slice() slice方法会生成新的数组
const newLs4 = Array.prototype.slice.call(arguments)
const newLs5 = Array.prototype.splice.call(arguments, 0)
console.log(newLs1)
console.log(newLs2)
console.log(newLs3)
console.log(newLs4)
console.log(newLs5)
}
a(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7)箭头函数不绑定arguments
- 箭头函数没有arguments 属性
js
function a(p1, p2, p3, p4 = 4, ...args) {
return (a1) => {
console.log(arguments) // 箭头函数没有arguments 熟悉因此获取当前this为最外层函数的
}
}
a(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7)(10) // [Arguments] { '0': 1, '1': 2, '2': 3, '3': 4, '4': 5, '5': 6, '6': 7 }使用es6 剩余参数 还是es5 arguments
- 剩余参数只包含那些没有对应形参的实参,剩余参数是一个真正的数组,可以进行数组的所有操作
- arguments 对象包含了传给函数的所有实参; arguments对象不是一个真正的数组
- arguments是早期的ECMAScript中为了方便去获取所有的参数提供的一个数据结构,而rest参数是ES6中提供并且希望以此来替代arguments的
callee
arguments的主要用途是保存函数参数,但这个对象还有一个名叫callee的属性,该属性是一个指针,指向拥有这个arguments对象的函数。
用途可以在递归的时候让代码更加解耦
- 递归方法
js
function factorial(num){
if(num<=1){
return 1;
}else{
return num * factorial(num-1);
}
}- 如果是函数表达式或者是用其他函数接收递归函数调用
js
const test = function (num){
if(num<=1){
return 1;
}else{
return num * arguments.callee(num-1);
}
}
console.log( test(10))